고려대학교 강필성교수님 강의를 짧게 정리하였습니다.
[2003] NNLM (Neural Network Language Model)
- Purpose : one-hot vector의 curse of dimensionality를 해결하겠다.
- 각 word는 distributed word feature vector 로 표현할 수 있다.
- word sequences in terms 의 probability function로 표현할 수 있다.
- probability function의 parameters와 word feature vectors를 동시에 할 수 있다.
- Why it works?
- similar roles (semantically and synthetically)에서 문장을 generalize 할 수 있다.
- Comparison with Count-based Language Models
- Chain rule 이용
그렇지만 만약 1~100 word가 있을 때 100번째를 보려면 99번째까지를 계산해야함. (정확하게 99개의 같은 sequence를 가지는 단어를 찾기는 거의 불가능에 가까움)
→ Markov assumption : 기존의 몇개에 대해서만 보기로 하자. (n-grams)
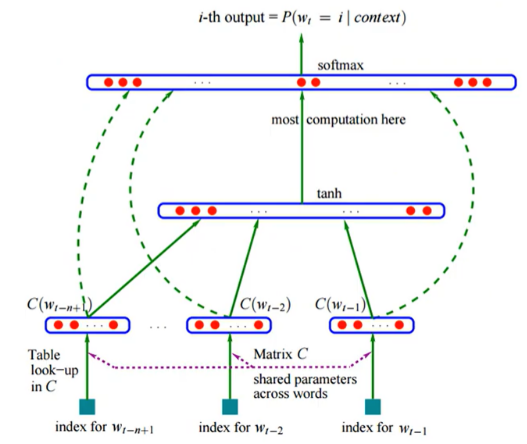
- Learning NNLM
- 전체 단어가 아니라 전체 window에 해당하는 문장 또는 문서의 sequence가 아니라 (e.g. 5-gram일 때) 앞서 4개의 단어를 보고 5번째 단어가 생성될 때의 확률이 극대화 되게 하는 것.
- 어떤 조건에서도 이후 단어들이 생성될 확률의 총 합은 1이다.
- 각 단어가 생성될 확률은 0보다 크거나 같아야한다.
- The free parameters of the model
y = b + Wx + U*tanh(d+Hx)
- the output bias b ( /V/ elements)
- the hidden layer biased d (with h elements)
- the hidden-to-output weights U (a /V/ by h matrix)
- the word features to output weigths W (a /V/ by (n-1)m matrix)
- the hidden layer weight H (a h by (n-1)m matrix)
학습은 stochastic gradient ascent 사용하여 계산
[2013] Word2Vec
- Two Architectures
- Continuous bag-of-words(CBOW) vs. Skip-gram

Skip-gram이 performance가 좋은걸로 알려져 있다.
- Learning representations : Skip-gram
approach
- Predict surrounding words in a window of length m of every word
- activation이 없다. (linear 연결)
- Objective function
- 중심 단어가 주어질 때, 어떤 context word의 log probability 최대화
- Learning strategy : Do not use all nearby words, but one per each training
- The number of weights to be trained : 2xVxN (Huge network)
- word pairs and phrases → as a single "word"
- subsampling frequent words
- negative sampling : 모든 단어의 weights를 update 하는 대신, few words(대략 5~20개)만 update 하기 (계산의 효율성을 위해)
[2014] GloVe
- Limitations of Word2Vec
- 매우 빈번하게 자주 사용되는 overwhelming 단어에 대해 시간을 많이 사용한다. (e.g. the)
- GloVe
- Based on matrix factorization method
- Notation

[2016] FastText
- Limitations of NNLM, Word2Vec and GloVe
- ignores the morphology or word by assigning a distinct vector to each word
- morphologically rich languages 에 대해서는 적용하기 어렵다. 형태소 변화가 다양한, 빈도가 낮은 언어에 대해서는 적용하기 어렵다.
- Goal
- Character n-grams 에 대해 prepresentation 학습 시키자
- 어떤 word의 분산표상(distributed feature) n-gram vector의 sum으로 표현하자
- Subword model
- Negative sampling in Word2Vec 에서는 score 이 단지 dot product between the two embeddings
→ Represent a word by the sum of the vector representations of its n-grams
e.g. apple
≪a≫
≪ap≫
≪app≫
≪appl≫
≪apple≫
= 전부 sum
- n-gram representation
keep all the n-grams of size 3,4,5 and 6
character의 sequence가 같아도 얼마만큼의 단어 또는 길이의 n-gram을 사용하느냐에 따라 서로 다른 vector가 assign
'Lecture Review > DSBA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [2014] Seq2Seq Learning with Neural Networks (0) | 2022.03.16 |
|---|---|
| Topic Modeling - 2 (0) | 2022.03.16 |
| Topic Modeling - 1 (0) | 2022.03.08 |
| Dimensionality Reduction (2) | 2022.03.04 |
| Doc2Vec & Others (0) | 2022.03.02 |